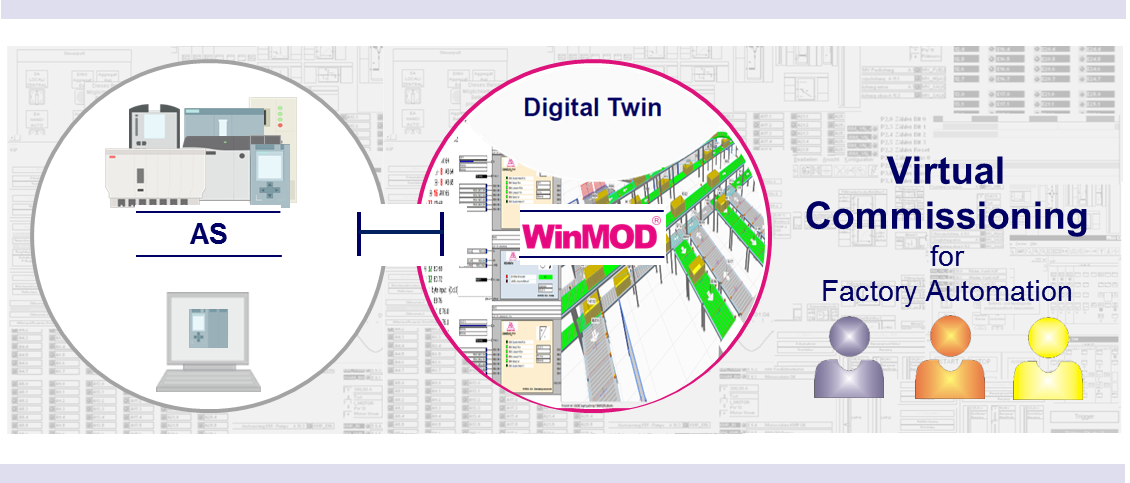
Virtual Commissioning
The Virtual Commissioning corresponds to the current state of practice of a real commissioning with a virtual machine or plant. The connected automation system can be real (HIL) or virtual (SIL).
Since 2002, WinMOD Systems for Virtual Commissioning has been used in industrial practice. They were the basis for the feasibility that has proven itself in thousands of projects.
Why Virtual Commissioning?
In practice, commissioning a real plant requires several different tasks to be mixed.
- subsequent clarification on the actual functionality of components and systems
- continuation of software development during commissioning
- functional test of the software with the real system
- parameterization and optimization of the automation software with the real plant
- briefing of the operator and the service staff
These work tasks are very indefinite in time. They are costly because they take place on-site, they are risky and they can drastically delay scheduled start-up appointments.
The innovative alternative is Virtual Commissioning (VC). In terms of content, it is a real commissioning of the real controller and the original software in conjunction with a virtual machine/system. The virtual machine/system has a sufficiently identical behaviour with respect to the controller in order to be able to put it into operation. The work contents of the commissioning can thus be carried out independently of the location and the state of completion together with the project participants.
Realization with WinMOD:
- The WinMOD Systems provide the conditions to model virtual machines/plants and connect them to the controllers.
- Virtual Commissioning is supported by high-performance online visualization, online forcing and parameterization and, if required, 3D visualization, material flow and robot simulation.
- Virtual Commissioning can be carried out in the remote location and, also if required, parallel to the real system.
Achievable Results:
- The Virtual Commissioning enables an early safeguard and optimization of the control programs and thus a shortening of development and commissioning times.
- Functional optimizations can be realized and the instruction of the users may already have taken place.
- Increases in efficiency and faster production start-ups through extensive validation from software to mechanics is the most important result.
